Atrial Fibrillation V Fib Ecg

In atrial fibrillation a fib the most common ekg abnormality.
Atrial fibrillation v fib ecg. The first upward pulse of the ekg signal the p wave is formed when the atria the two upper chambers of the heart contract to pump blood into the ventricles. Instead in several areas inside the atria form groups of excitable cells generate electrical impulses that fire simultaneously and spread throughout the atria causing a short circuiting effect see above. The mechanisms in ventricular fibrillation are as in atrial fibrillation existence of multiple re entry circuits which cause chaotic ventricular depolarization. In ventricular fibrillation there is no normal electrical activity.
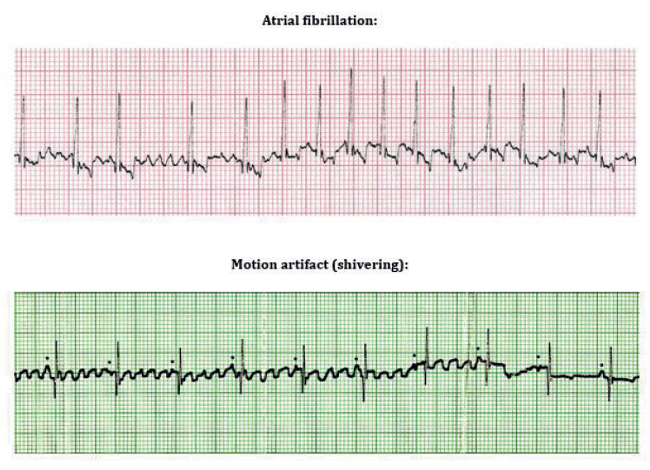
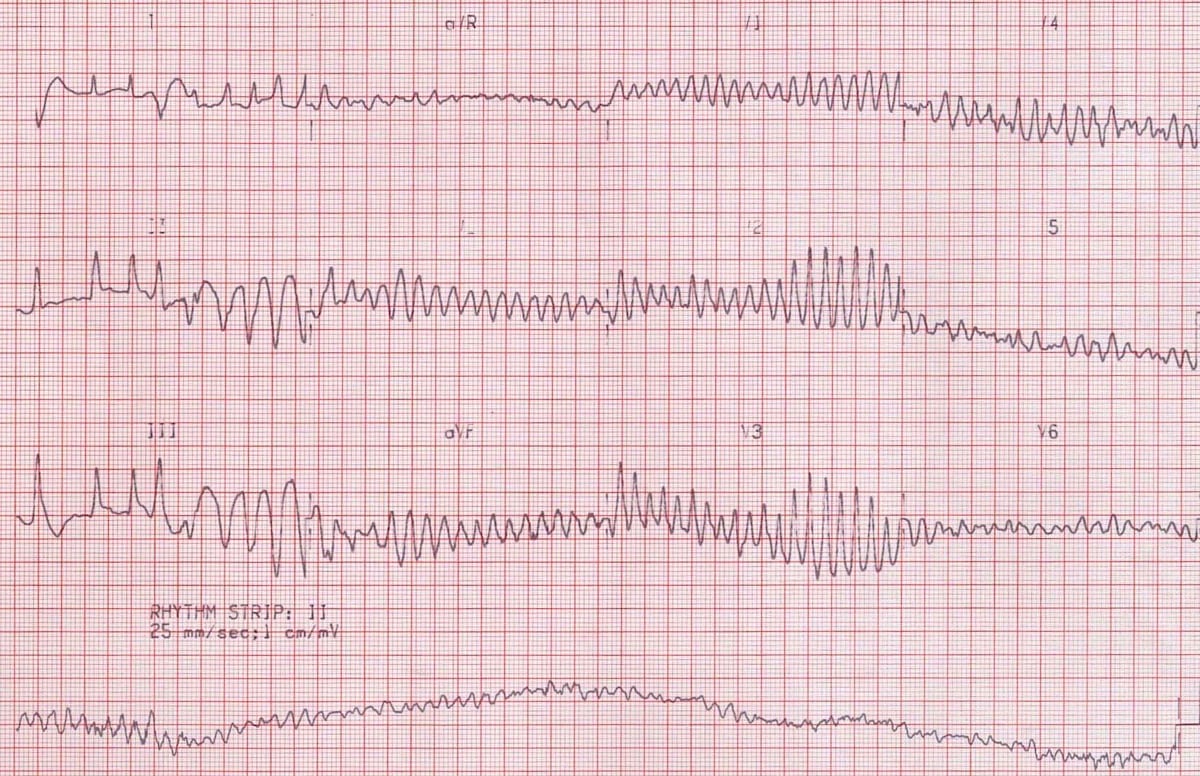
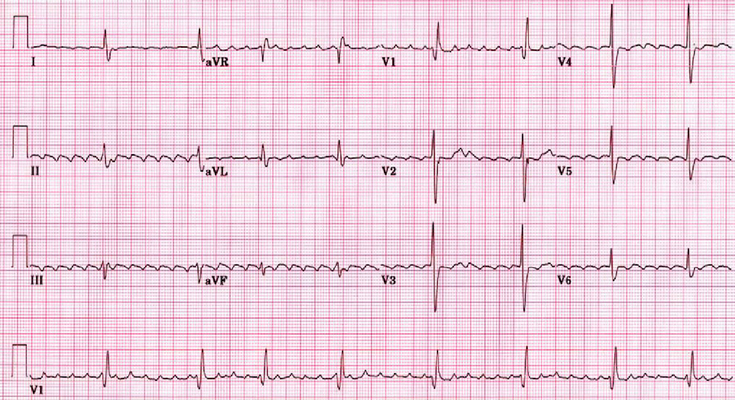
A characteristic sign of a fib is the absence of a p wave in the ekg signal. Atrial fibrillation is verified on the ecg resting ecg holter ecg event recorder. The prognosis is very poor with the majority of patients dying. In a fib you will see many fibrillation beats instead of one p wave.
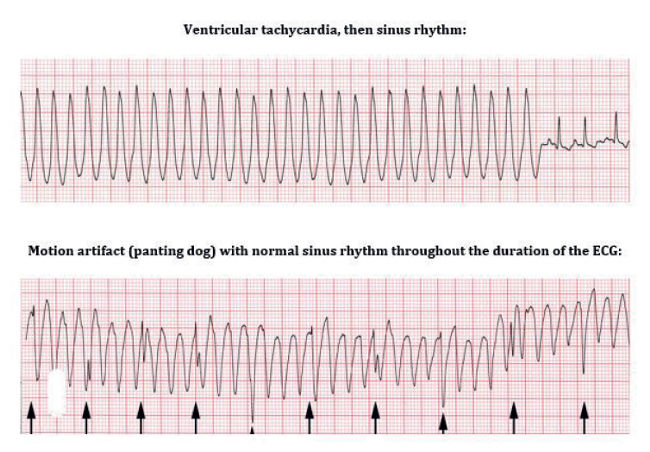
Common symptoms of afib are weakness dizziness anxiety and shortness of breath. In ventricular tachycardia v tach ventricles depolarize but pumping action is not effective. Can progress to v fib d. The electrical impulses do not travel in an orderly fashion through the atria as with normal conduction sinus rhythm.
In this atrial fibrillation ecg review the ecg criteria to diagnose atrial fibrillation afib including atrial fibrillation with rvr coarse atrial fibrillation and other af scenarios are. Holter ecg may be used to assess the number of arrhythmia episodes and occurrences or asymptomatic episodes. A fib is the most common type of irregular heart rhythm. Note almost normal qrs but missing p wave.
Atrial fibrillation is caused by irregular electrical impulses in the atria and ventricular fibrillation is caused by irregular electrical impulses in the ventricles. Mechanism of atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation afib and ventricular fibrillation vfib are both heart conditions that are referred to as arrhythmias. The patient dies if the rhythm is not restored.
If the patient may have coronary heart disease exercise stress test exercise ecg should be considered. Focal activation in which af originates from an area of focal activity. Symptoms of both afib and vfib are shortness of breath dizziness nausea and chest pain. This activity may be triggered due to increased automaticity or from micro.
Absence of contractions causes syncope and circulatory collapse. Atrial fibrillation afib and ventricular fibrillation vfib are both a type of abnormal heart rhythm arrhythmia. The mechanisms underlying af are not fully understood but it requires an initiating event focal atrial activity pacs and substrate for maintenance i e.