1 2 Vs 1 4 Addition
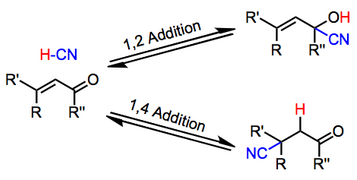
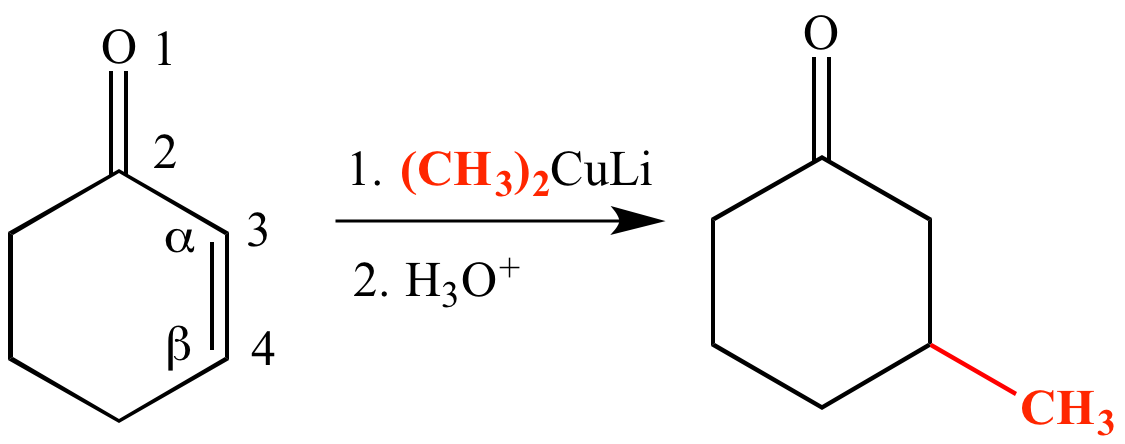
Simple alkene compounds do not show 1 2 reactivity due to lack of polarity unless the alkene is activated with special substituents with α β unsaturated carbonyl compounds such as cyclohexenone it can be deduced from.
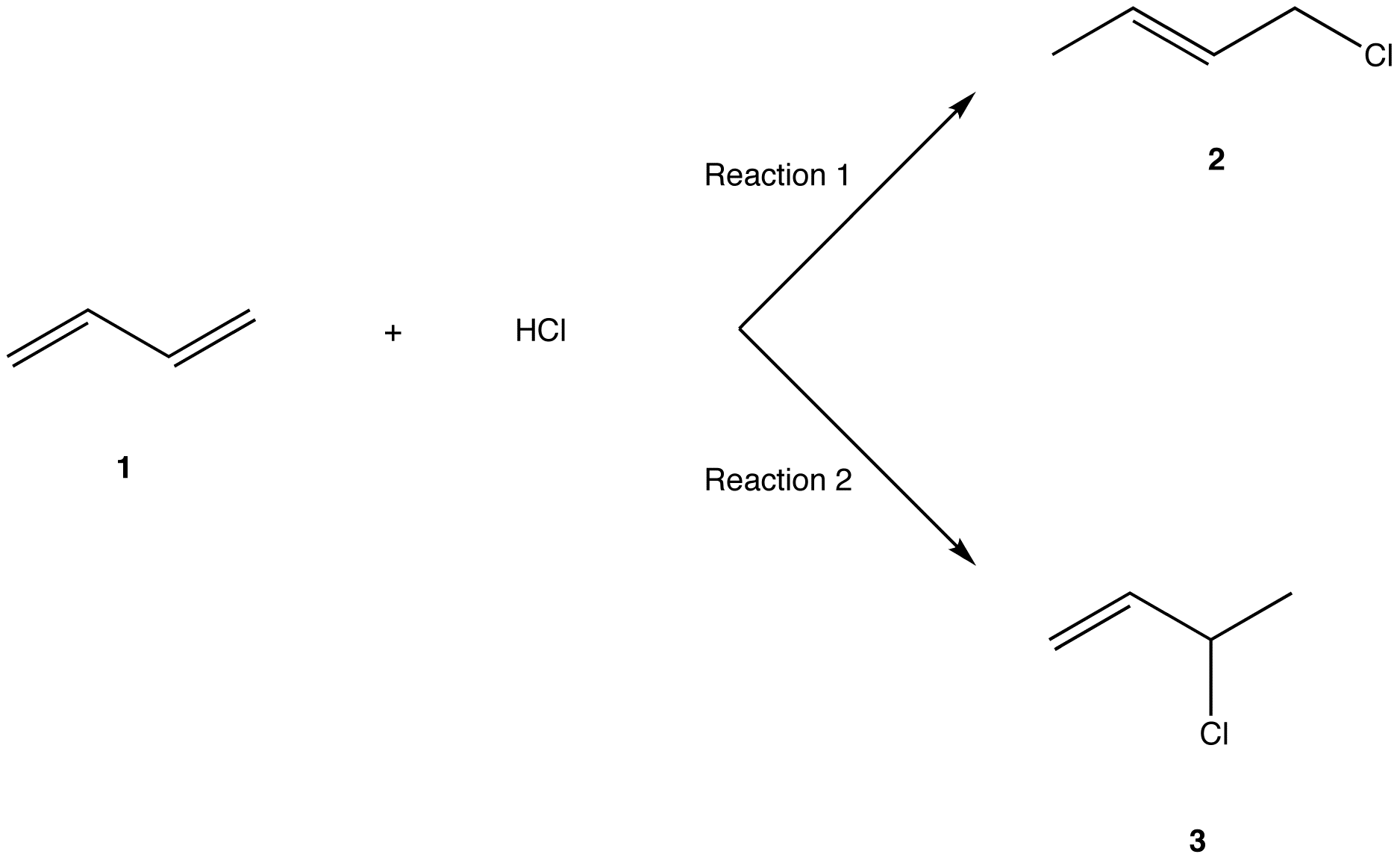
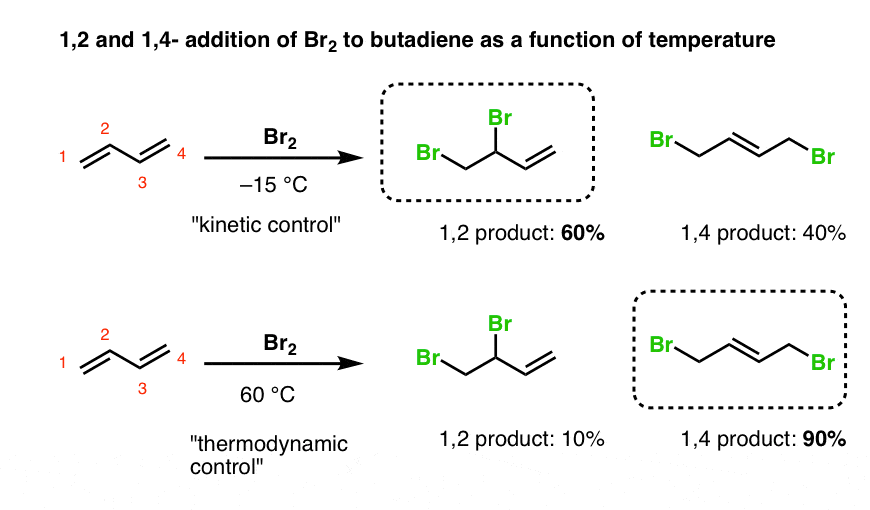
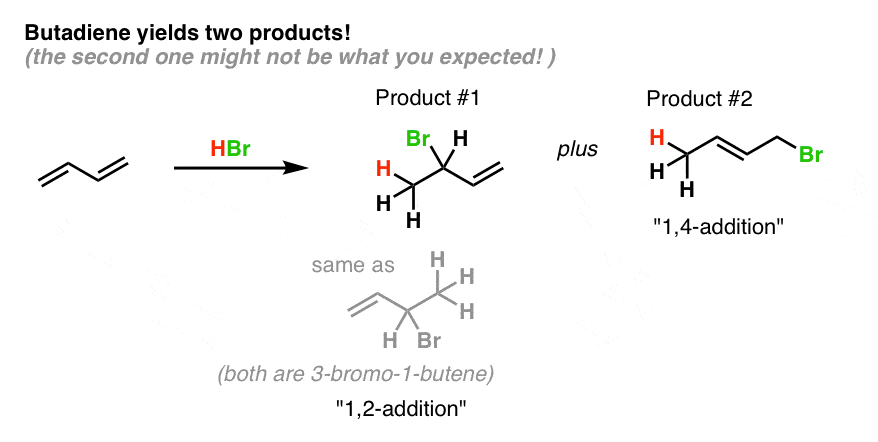
1 2 vs 1 4 addition. In reaction 1 the net reaction is addition of a hydrogen atom to c 1 and a chlorine atom to c 4 in 1. Recent progress in copper i catalysed addition of grignard reagents is reviewed throughout this chapter comparing and contrasting the well established 1 4 selectivity of cu i ligand complexes with the newly. 1 4 addition is an electrophilic addition reaction of conjugate dienes. The regiochemistry changes when the reaction is carried out at lower temperatures.
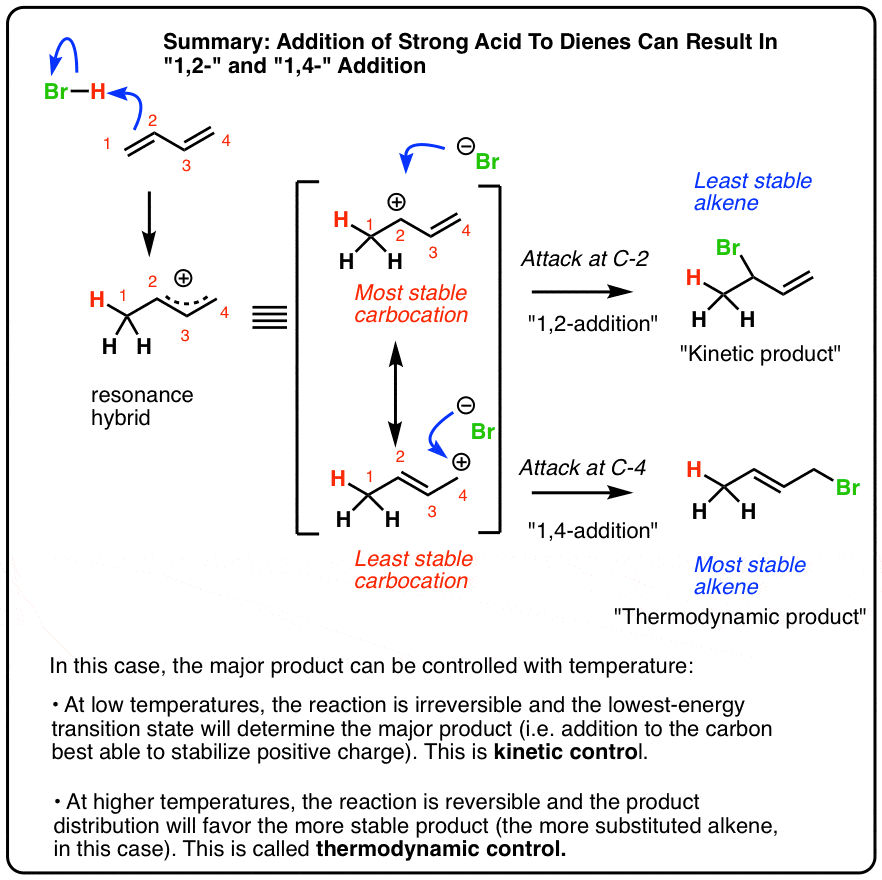
Bonding at the terminal carbon atoms of a conjugated diene with a shift of the remaining double bond to the 2 3 location these numbers refer to the four carbons of the conjugated diene and are not. Br are on adjacent carbons and br has added to the most substituted. The 1 4 adduct is the thermodynamic product of the reaction since it is the more stable product. The recent discovery that copper i is able to catalyse the asymmetric 1 2 addition of grignard reagents to α β unsaturated as well as aromatic ketones was a true revelation.
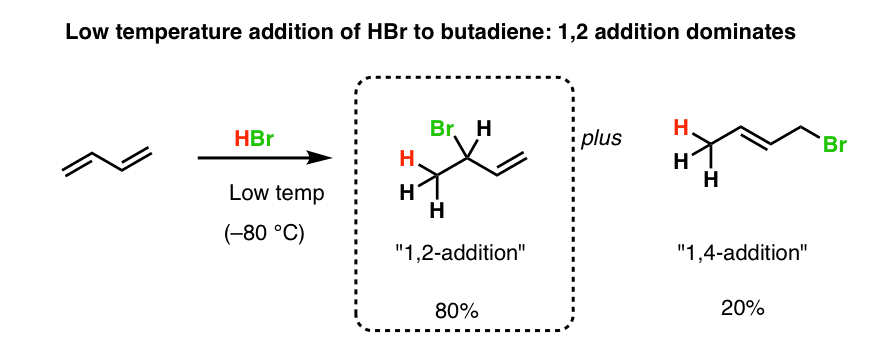
Nucleophilic conjugate addition is a type of organic reaction ordinary nucleophilic additions or 1 2 nucleophilic additions deal mostly with additions to carbonyl compounds. The effect of temperature. Two electrophilic addition reactions could occur between 1 3 butadiene 1 and hydrogen chloride. For example the addition of hydrogen bromide to 1 3 butadiene at temperatures below zero leads mainly to the 1 2 addition product while addition reactions run at temperatures above 50 c with these chemicals produces mainly the 1 4 addition product.
Hence reaction 1 is called 1 4 addition and its product 2 1 4 adduct. One of the confusing parts of diene chemistry is the fact that they can product multiple products specifically 1 2 addition products and 1 4 addition products. The 1 2 addition starts predominating because of the proximity effect. Bonding to the adjacent carbons of a double bond the unexpected product comes from 1 4 addition i e.
Whether more 1 2 addition or 1 4 addition product is created depends largely on the temperature at which the reaction is run. 1 4 addition to dienes and kinetic control vs thermodynamic control to recap. Dienes undergo two major reactions which include diels alder reactions and electrophilic addition usually of hcl or hbr but other groups are possible.