1 2 Addition Vs 1 4 Addition Carbonyl

Epub 2019 jul 17.
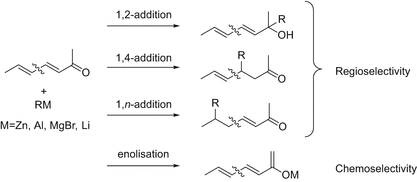
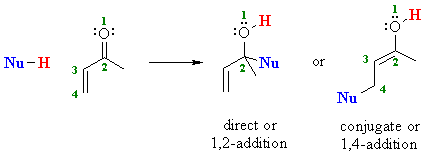
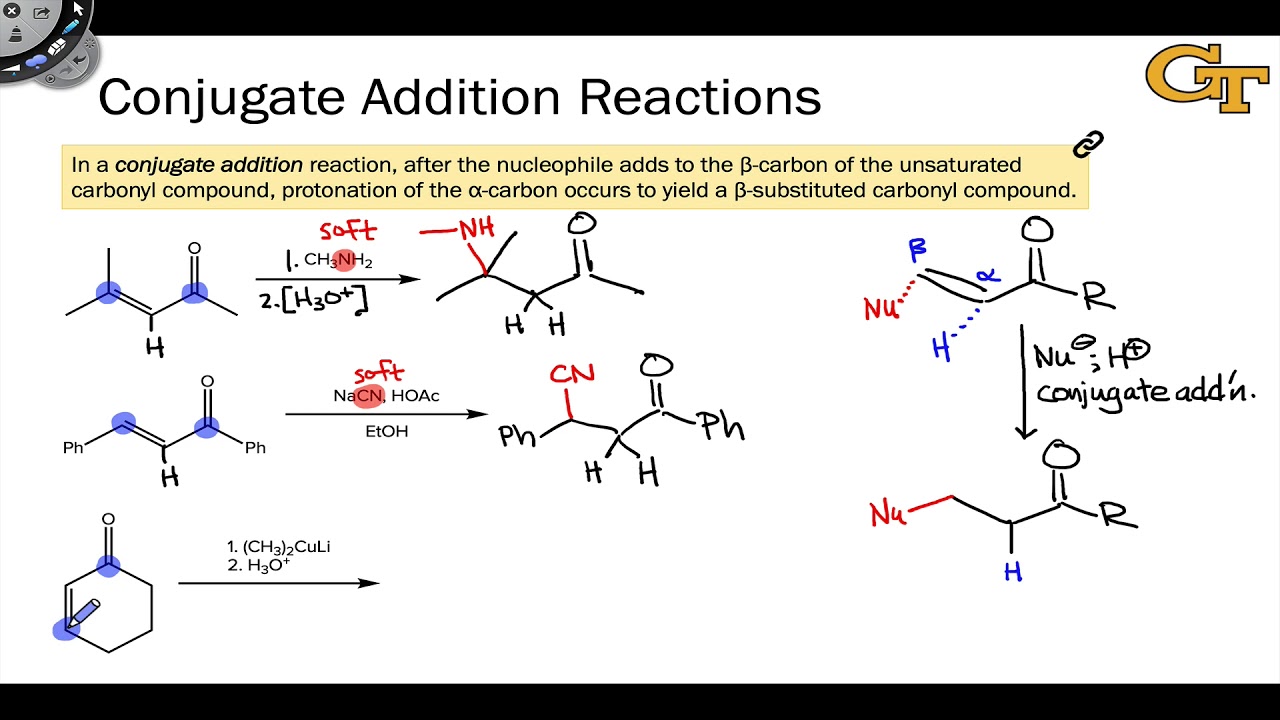
1 2 addition vs 1 4 addition carbonyl. 1 in the. Whether 1 2 or 1 4 addition occurs depends on multiple variables but mostly it is determined by the nature of the nucleophile. Remember an allylic carbocation is when a carbocation forms one bond away from a double bond. 1 2 and 1 4 additions to carbonyls some of the earliest attempts to understand stereoselectivity in organic reactions were the rationalizations and predictive models made in the early 1950s by curtin 1 cram 2 and prelog 3 to explain the addition of achiral nucleophiles such as grignard reagents to the diastereotopic faces of ketones and aldehydes having a proximal stereocenter.
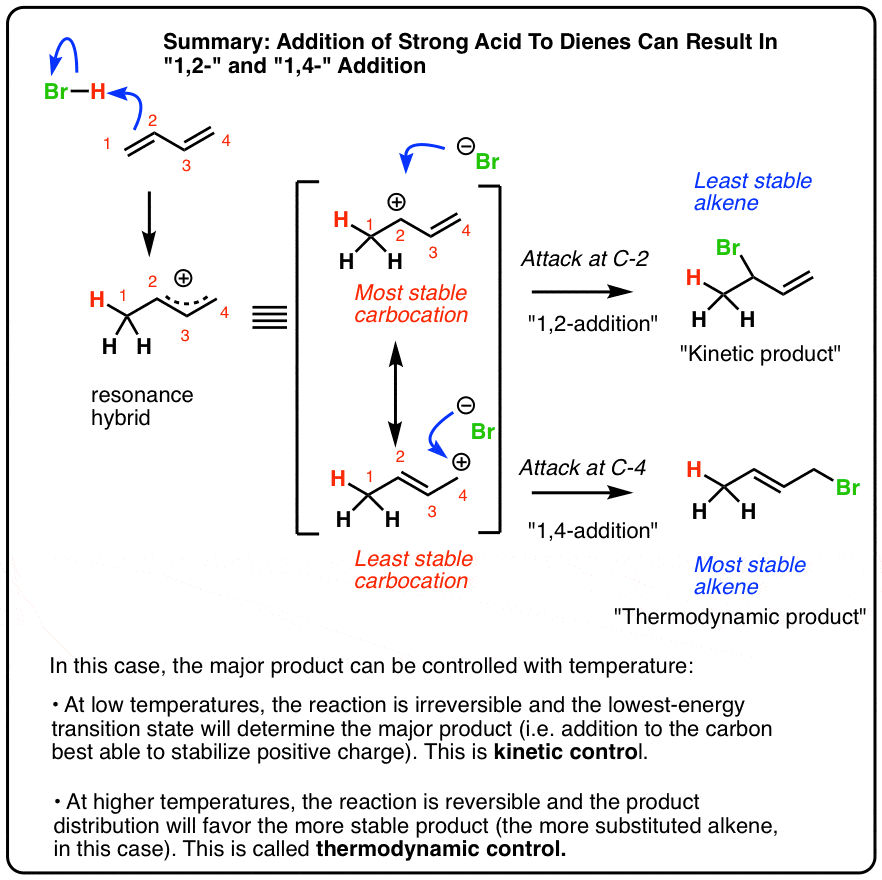
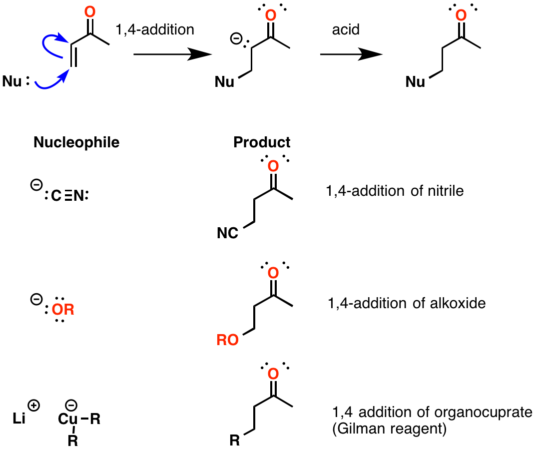
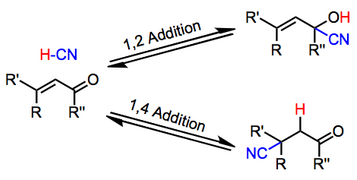
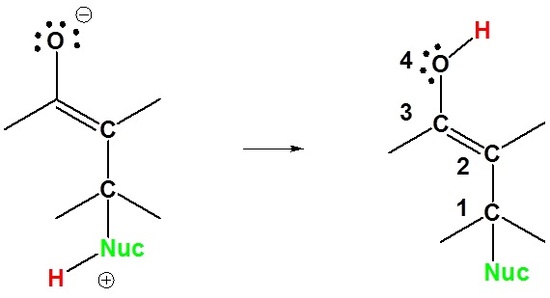
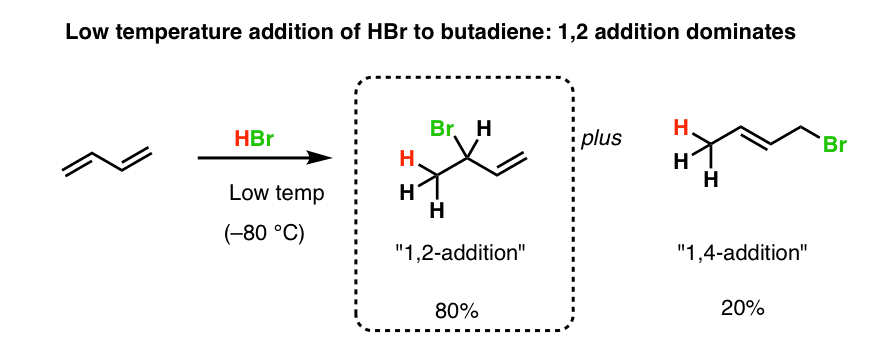
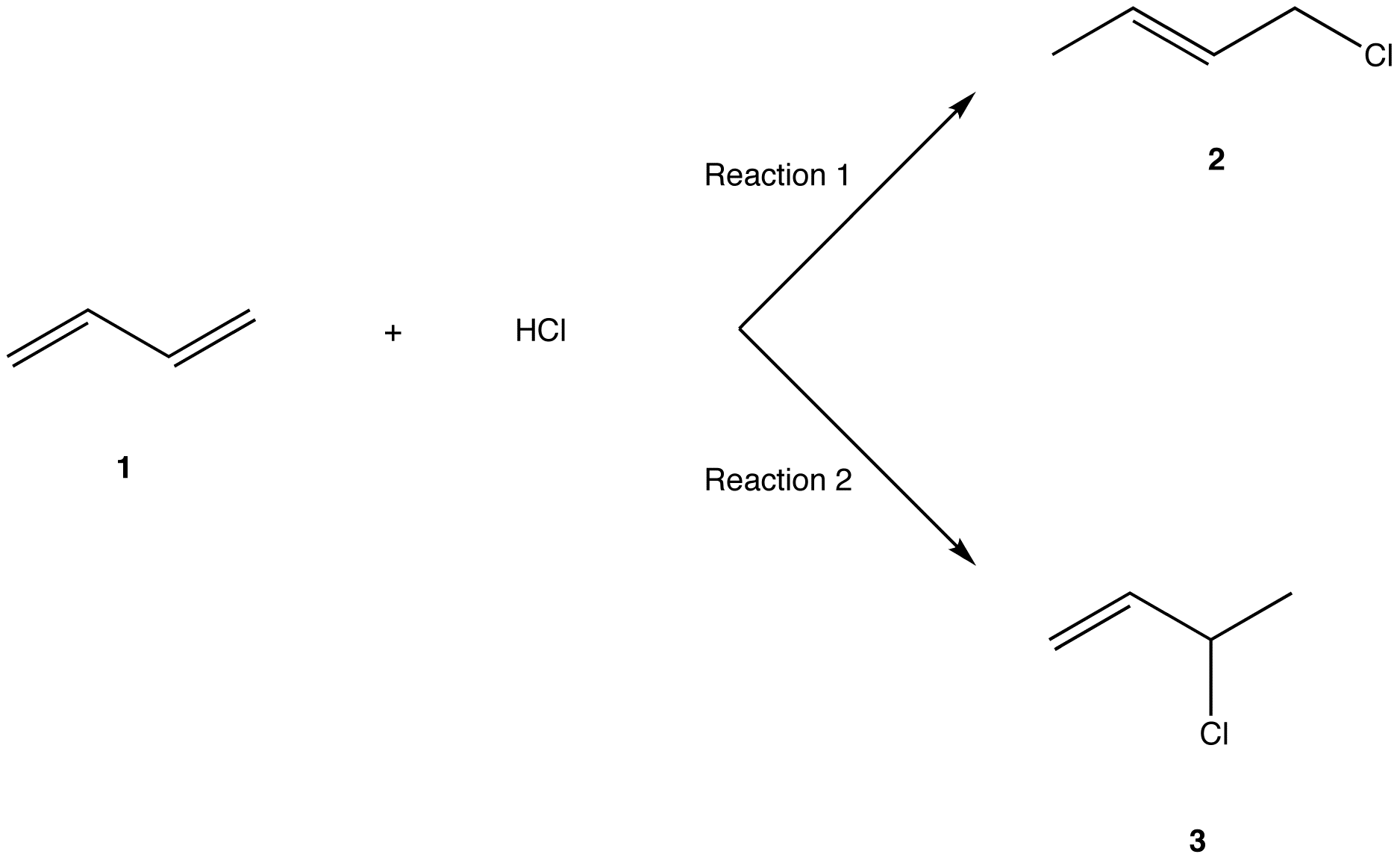
The reason for observing two products is due to the stability of the allylic carbocation intermediate. Authors su yong shim. In a nucleophilic attack on an α β unsaturated carbonyl compound both 1 2 and 1 4 addition can occur. The recent discovery that copper i is able to catalyse the asymmetric 1 2 addition of grignard reagents to α β unsaturated as well as aromatic ketones was a true revelation.
Conditions and reaction mechanism for 1 2 and 1 4 addition. The two observed products consist of a 1 2 addition of hbr and a 1 4 addition of hbr to the diene. In this account we summarize our recent studies on cobi catalyzed asymmetric nucleophilic carbonyl addition and tandem reactions. So you need to learn under which conditions the michael addition takes precedence.
Enantioselective carbonyl 1 2 or 1 4 addition reactions of nucleophilic silyl and diazo compounds catalyzed by the chiral oxazaborolidinium ion acc chem res. During the addition of a nucleophile there is a competition between 1 2 and 1 4 addition products.